
Clinical Report with R
R for TFL
Tao Xiang
2024-07-26
Preface
This is a presentation for R users in all-levels.
We will focus on how to apply R programming into our daily TLF, rather than deconstructing R codes in TLF
Feel free to interrupt if any question during presenting
Outline
In this workshop, four topics will be presented:
- Introduction to R & R markdown (15 min)
- Frontier of R for TLFs in pharmaceutical industry (15 min)
- Creating TLFs with R to PDF (30 min)
- Creating TLFs with R to RTF (30 min)
What is R/RStudio/R Markdown?
R is a language and environment for statistical computing and graphics. It is a GNU project which is similar to the S language and environment which was developed at Bell Laboratories.
RStudio is an integrated development environment (IDE) for R and Python. It includes a console, syntax-highlighting editor that supports direct code execution, and tools for plotting, history, debugging, and workspace management.
R Markdown: Computing language + Authoring language (R + Markdown) to generate reproducible high-quality reports
Why R?

Free to use in your local laptop forever

Open-source is always be appreciated
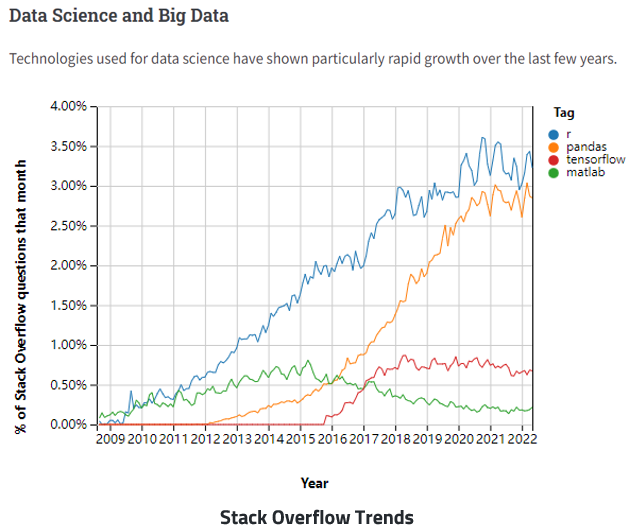
R gains popularity in Big Data Era
R Events in Pharma
- R/Pharma conferences and events were sponsored by Phuse since 2018
- More topics about R/R Shiny in PharmaSUG Events
- PharmaRUG in China since 2023
R-Based Submission Package Submitted to FDA (Publicly Available)
Three submission pilot
- RConsortium/submissions-pilot1-to-fda: A respiratory in GitHub demonstrates the eCTD submission package, an FDA official response letter with statistical review and evaluation is also covered in this repo
- RConsortium/submissions-pilot2-to-fda: A respiratory in GitHub tests the concept that a Shiny application created with the R-language can be bundled into a submission package and transferred successfully to FDA reviewers. (Finished)
- RConsortium/submissions-pilot3-to-fda: A respiratory in GitHub expands on the work done in submission Pilot 1 by utilizing R to generate ADaM datasets
Novo Nordisk’s journey to an R-based FDA submission (Details are unpublic)
Create and Output Tables/Figures with R
General Ways
Create and Output Tables/Figures with R
Packages developed by Pharma
Concept for creating tables in R
- Create a data.frame
- Transform 2-dimensional data to an table object (R list with attributions for output)
- Format table in correlated list blocks
- Translate/Encode to desired format (HTML, LaTeX, RTF)
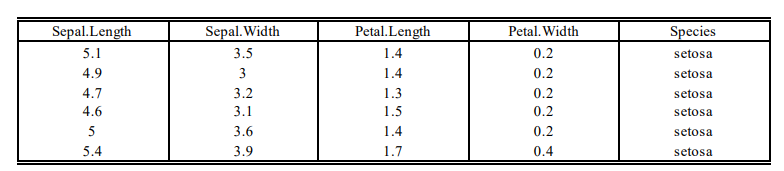
Simple gt table example
| Iris Data | ||||
| A Subtitle | ||||
| Sepal.Length | Sepal.Width | Petal.Length | Petal.Width | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.1 | 3.0 | 5.9 | 2.1 | virginica |
| 7.6 | 3.0 | 6.6 | 2.1 | virginica |
| 7.3 | 2.9 | 6.3 | 1.8 | virginica |
| 7.2 | 3.6 | 6.1 | 2.5 | virginica |
| 7.7 | 3.8 | 6.7 | 2.2 | virginica |
| 7.7 | 2.6 | 6.9 | 2.3 | virginica |
| 7.7 | 2.8 | 6.7 | 2.0 | virginica |
| 7.2 | 3.2 | 6.0 | 1.8 | virginica |
| 7.2 | 3.0 | 5.8 | 1.6 | virginica |
| 7.4 | 2.8 | 6.1 | 1.9 | virginica |
| 7.9 | 3.8 | 6.4 | 2.0 | virginica |
| 7.7 | 3.0 | 6.1 | 2.3 | virginica |
Simple rtables example
suppressPackageStartupMessages(
library(rtables)
)
lyt <- basic_table() %>%
split_cols_by("ARM") %>%
analyze(c("AGE", "BMRKR1", "BMRKR2"), function(x, ...) {
if (is.numeric(x)) {
in_rows(
"Mean (sd)" = c(mean(x), sd(x)),
"Median" = median(x),
"Min - Max" = range(x),
.formats = c("xx.xx (xx.xx)", "xx.xx", "xx.xx - xx.xx")
)
} else if (is.factor(x) || is.character(x)) {
in_rows(.list = list_wrap_x(table)(x))
} else {
stop("type not supported")
}
})
build_table(lyt, ex_adsl) A: Drug X B: Placebo C: Combination
------------------------------------------------------------
AGE
Mean (sd) 33.77 (6.55) 35.43 (7.90) 35.43 (7.72)
Median 33.00 35.00 35.00
Min - Max 21.00 - 50.00 21.00 - 62.00 20.00 - 69.00
BMRKR1
Mean (sd) 5.97 (3.55) 5.70 (3.31) 5.62 (3.49)
Median 5.39 4.81 4.61
Min - Max 0.41 - 17.67 0.65 - 14.24 0.17 - 21.39
BMRKR2
LOW 50 45 40
MEDIUM 37 56 42
HIGH 47 33 50 Simple r2rtf example
Experience 1: TFL in PDF with R
Inspired by R-based pilot submission in late 2021, I started to exploring the way to create TLF with R which can visually be compatible with SAS ODS outputs template in 2022. As a fan of r markdown, I made the first breakthrough by applying tidyverse on markdown to generate ICH style tables.
Structure of R markdown
It contains three important types of content:
- An (optional) YAML header surrounded by —s.
- Chunks of R code surrounded by ```.
- Text mixed with simple text formatting like # heading and italics.
---
title: "Sample RMD"
date: 2022-02-22
output: pdf_document
---
Any plain text here.
```{r include = FALSE}
library(ggplot2)
diamonds %>%
ggplot(aes(carat)) +
geom_freqpoly(binwidth = 0.01)
```R markdown workflow (knit the document)
Precisely, R markdown is pandoc’s markdown. It combines plain text and R codes (maybe other language code) together, use knitr package as core to create a md file which includes the code and its output. The markdown file generated by knitr is then processed by pandoc, http://pandoc.org/, which is responsible for creating the finished file.

A highly customized CSR table with RMD
Prerequisite
Please use Rstudio as IDE, and install the required R packages at the first
install.packages("tidyverse") #Modern R data manipulation scheme, include a bunch of essential packages
install.packages("rmarkdown") #R markdown ecosystem
install.packages("haven") #Import and export SAS files, also support SPSS, STATA files
install.packages("tinytex") #Help to install and maintain Tex Live , and Compile LaTeX Documents
install_tinytex() #Downloads and installs TinyTeX, a custom LaTeX distribution based on TeX LiveElements to construct a table
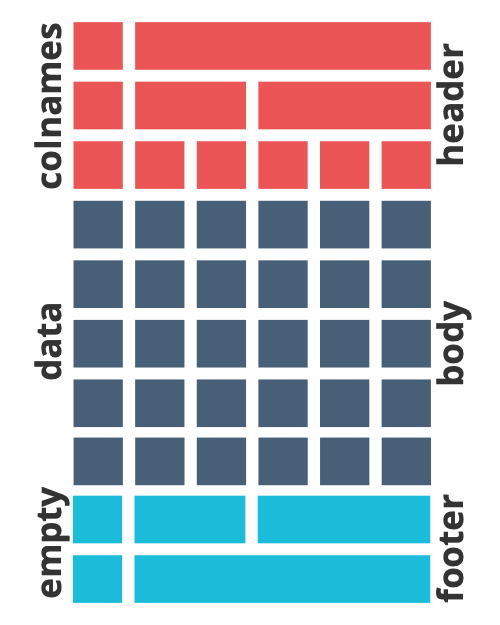
Our shell and table template are always constructed by 3 part:
Header + body + footer
In LaTeX, this is a frequently used format with developed package fancyhdr
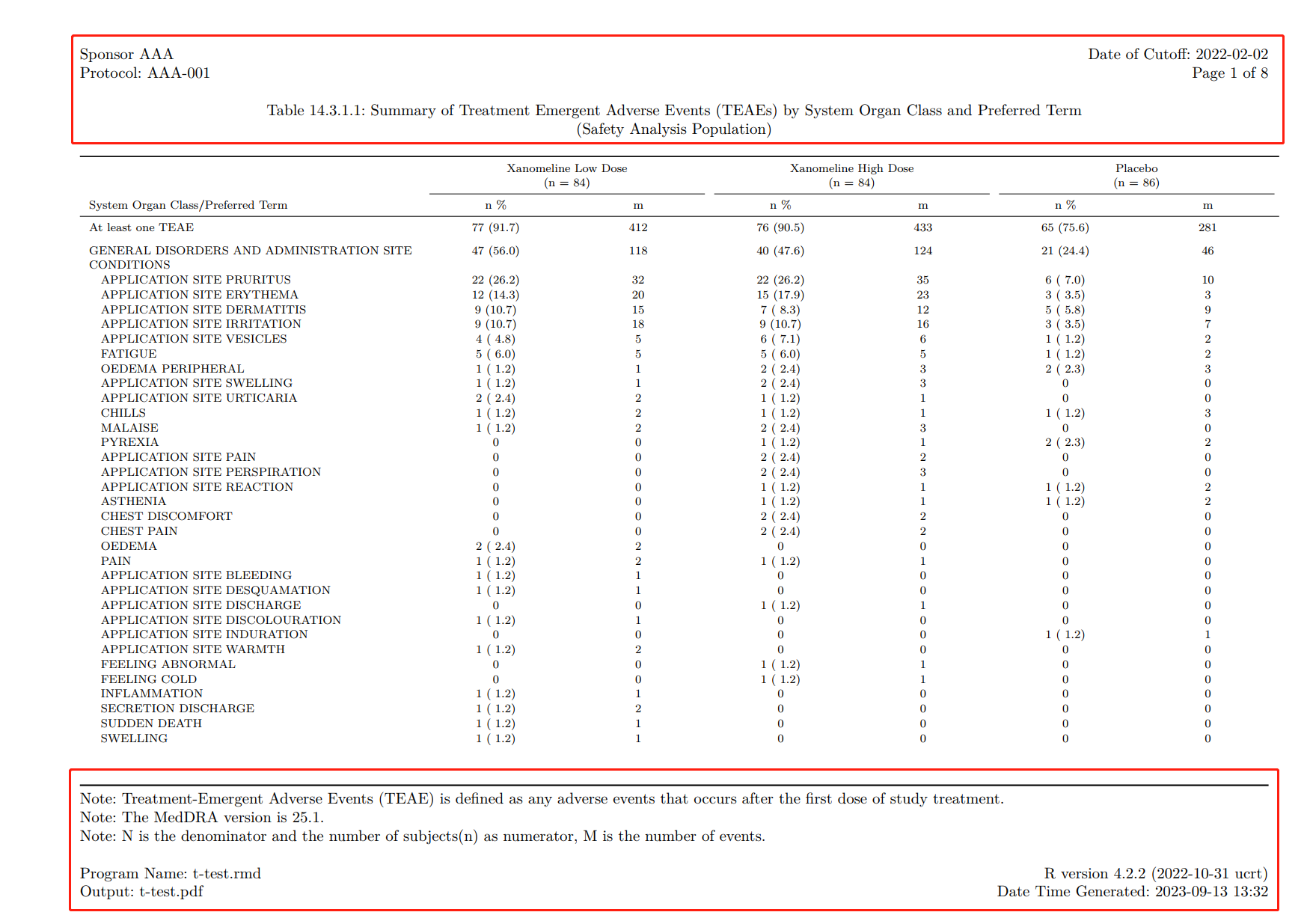
Table elements
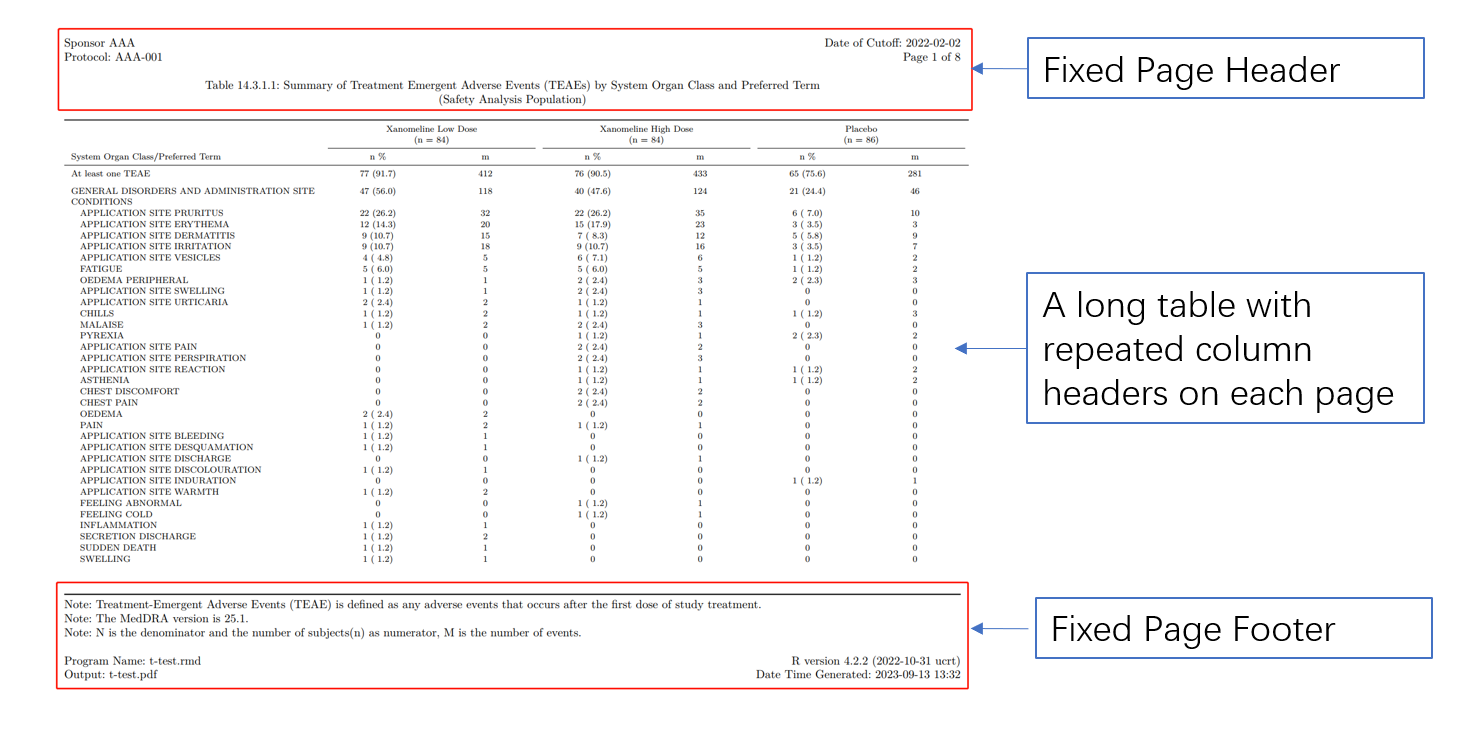
Include header and footer with YAML
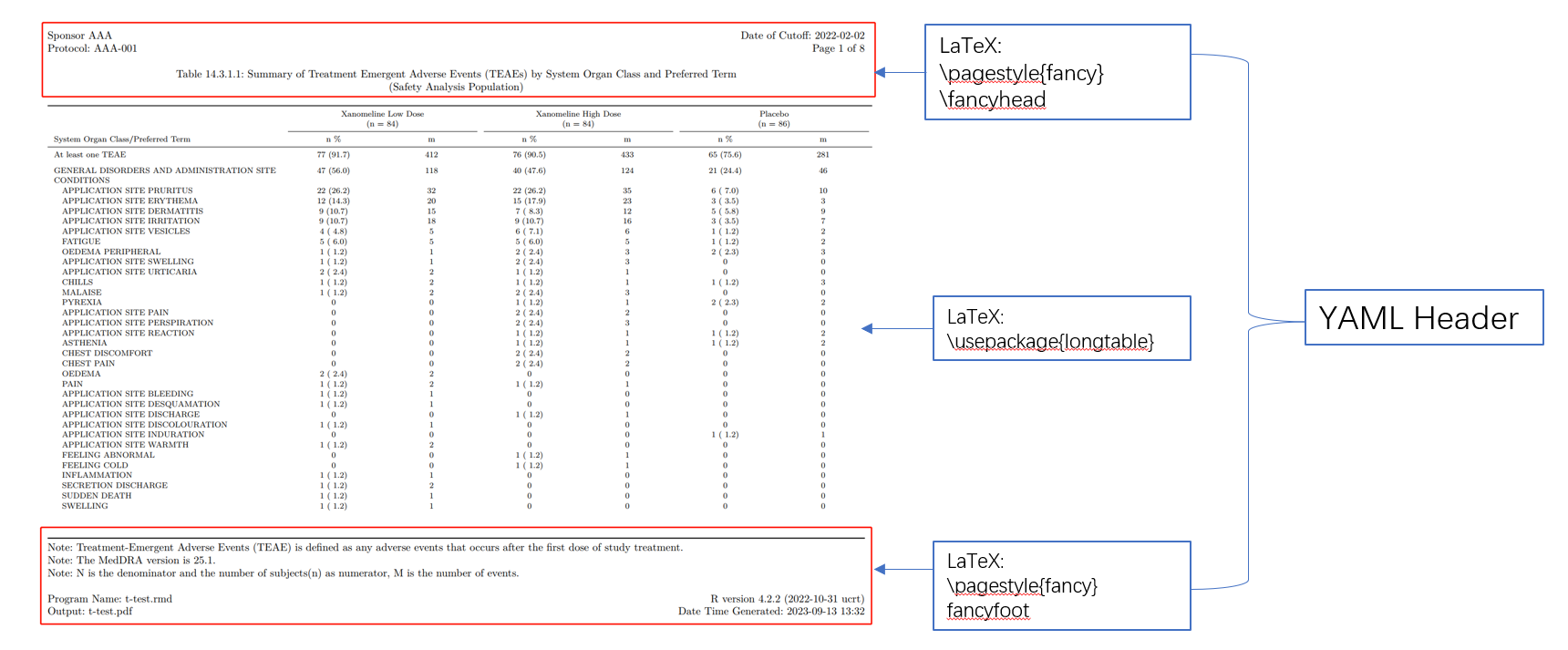
YAML header for table template
Here is a full yaml header we write for this table, we include some LaTex packages to enhance the output and also embed the header and footer in it.
---
documentclass: report
classoption:
- landscape
papersize: a4
geometry:
- left=0.75in
- right=0.375in
header-includes:
- \usepackage{longtable}
- \usepackage{array}
- \usepackage{multirow}
- \usepackage{wrapfig}
- \usepackage{float}
- \usepackage{colortbl}
- \usepackage{pdflscape}
- \usepackage{tabu}
- \usepackage{threeparttable}
- \usepackage{threeparttablex}
- \usepackage[normalem]{ulem}
- \usepackage{makecell}
- \usepackage{xcolor}
- \usepackage{lastpage}
- \usepackage{datetime}
- \renewcommand{\dateseparator}{-}
- \yyyymmdddate
- \usepackage[nocheck]{fancyhdr}
- \pagestyle{fancy}
- \fancyhead[L]{ Sponsor AAA \hfill Date of Cutoff:\ 2022-02-02 \\ Protocol:\ AAA-001 \hfill Page \thepage\ of \pageref{LastPage} \newline \newline \centerline{Table 14.3.1.1:\ Summary of Treatment Emergent Adverse Events (TEAEs) by System Organ Class and Preferred Term} \\ \centerline{(Safety Analysis Population)}}
- \fancyfoot{}
- \fancyfoot[L]{ Note:\ Treatment-Emergent Adverse Events (TEAE) is defined as any
adverse events that occurs after the first dose of study treatment. \newline Note:\
The MedDRA version is 25.1. \newline Note:\ N is the denominator and the number
of subjects(n) as numerator, M is the number of events. \newline \\ Program
Name:\ t-test.rmd \hfill R version 4.2.2 (2022-10-31 ucrt) \\ Output:\ t-test.pdf \hfill
Date Time Generated:\ \today\ \currenttime}
- \renewcommand{\headrulewidth}{0pt}
- \renewcommand{\footrulewidth}{1pt}
- \usepackage[justification=centering, font=normalsize, labelformat=empty]{caption}
- \usepackage{booktabs}
- \renewcommand{\bottomrule}{}
output:
pdf_document:
latex_engine: xelatex
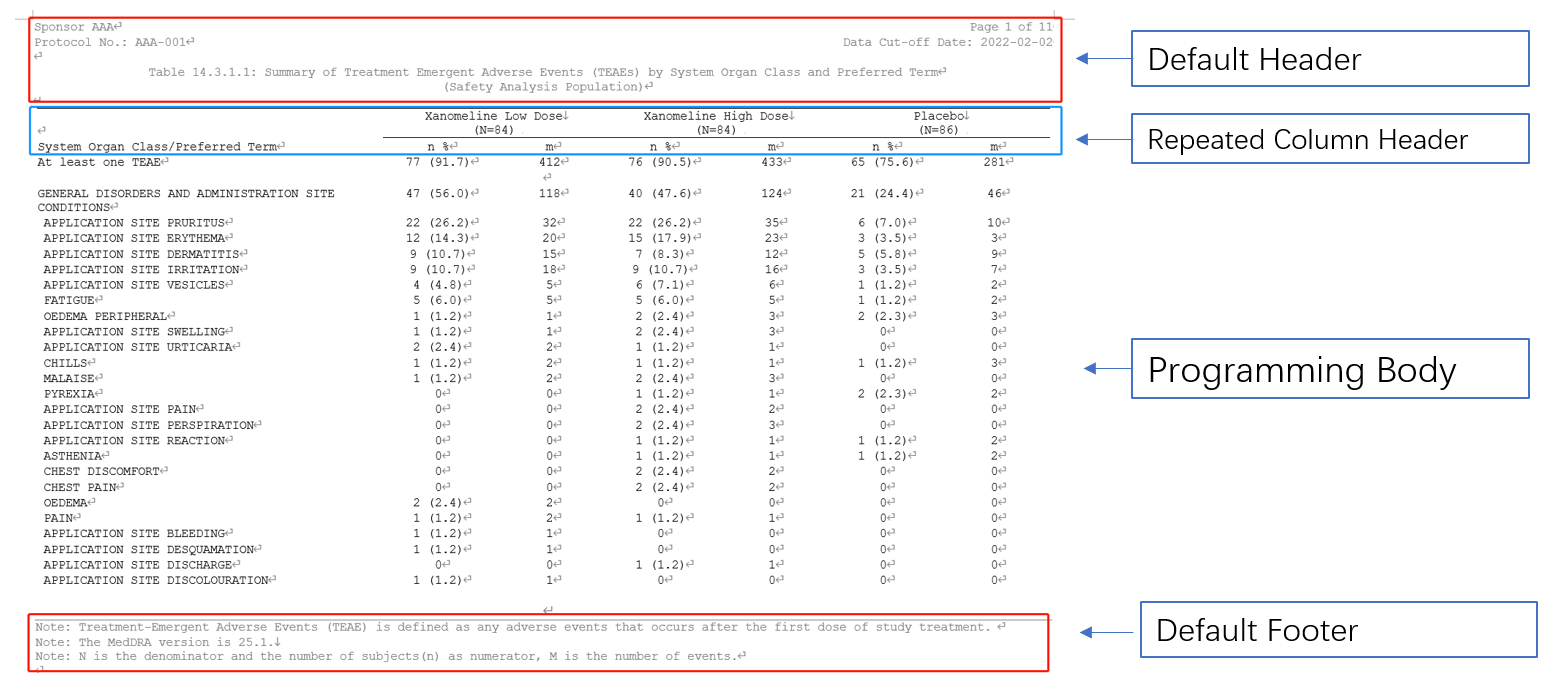
---Programming Body
- Required three packages for data manipulation, data import, output enhance
- Set project path and import analysis dataset
- Tidystyle programming with lots of steps to get final data just like SAS did
library(tidyverse)
library(haven)
library(kableExtra)
project_folder <- paste(str_split_1(getwd(), "/")[-length(str_split_1(getwd(), "/"))], collapse = "/")
path <- list(
adam = paste0(project_folder, "/adam"),
metadata = paste0(project_folder, "/metadata")
)
adae<-read_xpt(file.path(path$adam, "adae.xpt"))
adsl<-read_xpt(file.path(path$adam, "adsl.xpt"))
final <- analyze(
... #For dummy presenting
)Enhanced Output with knitr::kable() and kableExtra
output<- kable(final, longtable=T, booktabs=T, align='lcccccc',
escape=F,
caption=c("\\newline"),
col.names = linebreak(c("System Organ Class/Preferred Term","n \\%", "m", "n \\%", "m", "n \\%", "m"),
align = "c"),
linesep = sep_v
) %>%
add_indent(ind_num) %>%
add_header_above(c(" ", "Xanomeline Low Dose \n (n = 84)"=2, "Xanomeline High Dose \n (n = 84)"=2, "Placebo \n (n = 86)" = 2), line=T, bold = F) %>%
kable_styling(latex_options = c("repeat_header"),
font_size = 7.5,
position = "l",
repeat_header_text = "",
repeat_header_method = "append") %>%
column_spec(1, width = "2.9in") %>%
column_spec(2:7, width = "1.1in")
output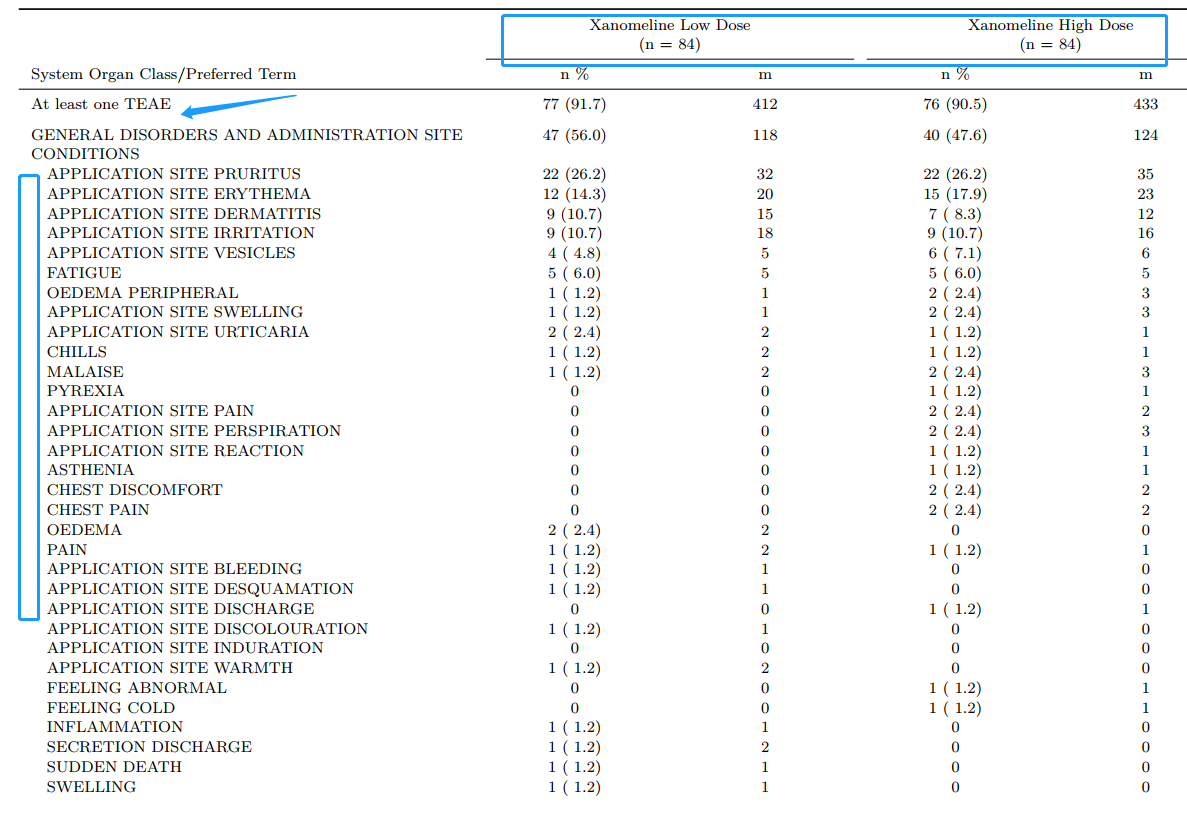
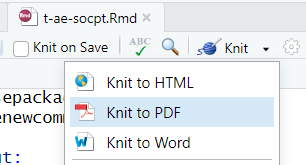
Render to PDF document
knit button (Ctrl + Shift + K)
In console:
rmarkdown::render("t-ae-socpt.Rmd", "t-ae-socpt.pdf")
Automatic template generator
TLF-start.ris a R script contained R codes to generateyamlheader automaticallyCode chunks includes several parts:
Set header information, cut-off date, program names and output name
Project path setup
Import title and footnote from metadata
Generate yaml header in rmd file
Advantages with TLF-start.r
Perfectly be compatible with our company’s shell and title_footnote metadata.
One metadata works for both SAS and R in production side, much easier for switching
Save times and keep template stable.
Roles with responsibility
Statisticians still write shell followed internal rules
![]()
Lead programmer should set up
TLF-start.rat the beginning of TLF work and applyread_tfl_titlefoot.sasto create metadata including all titles and footnotesProd/Dev programmer need to assign these objects in
TLF-start.rand run code when initiate each TLF.
Initiate or Update
TLF-start.rcould either initiate yaml header in a new Rmd file or update the template in working directory depends on the file existence
Hands-on presenting
Source ADaM datasets:
PHUSE CDISC Pilot replication ADaMs following ADaM IG v1.0
Github Respiratory: https://github.com/phuse-org/phuse-scripts/blob/master/data/adam/TDF_ADaM_v1.0.zip
Experience 2: TLF in RTF with R
Even PDF is a good document type for reviewing, RTF still plays a crucial rule for statistical analysis in pharmaceutical industry. R markdown generate nice and highly customized PDF/html outputs but have very limited support for RTF outputs. So, I have to find other ways to fulfill the requirements of customizing/generating RTF outputs.
Awesome combo: flextable + officer
![]()
flextablepackage provides a framework for easily creating tables for reporting and publications. Functions are provided to let users create tables, modify and format their content.officeris designed to produce content that is essentially composed of tables, graphs, and is ideal in cases for clinical reporting and automation of reporting in compliance with the official corporate templates
Prerequisite R packages
Be flexible to create tables with flextable
flextablecan easily create reporting table from data.frame. You can merge cells, add header rows, add footer rows, change any format and specify how data should be displayed in cells
SUBJID | TRT01P | AGE | SEX | RACE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1015 | Placebo | 63 | F | WHITE |
1023 | Placebo | 64 | M | WHITE |
1028 | Xanomeline High Dose | 71 | M | WHITE |
1033 | Xanomeline Low Dose | 74 | M | WHITE |
1034 | Xanomeline High Dose | 77 | F | WHITE |
1047 | Placebo | 85 | F | WHITE |
Table design
The concept of table design in flextable to RTF output is quite same as LaTex PDF we discussed in previous chapters. We can migrate the programming body part into this procedures as well. Create a flextable object and customize the column headers and data body.
RTF Template section
flextable::set_flextable_defaults(): Default properties contains the font family, the font size, padding, text alignment…, which will be used to flextable RTF outputs.officer::fpar(..., fp_p = fp_par(), fp_t = fp_text_lite(), values = NULL): Create a paragraph representation by concatenating formatted text or images.officer::ftext(text, prop = NULL): Format a chunk of text with text formatting properties (bold, color, …).officer::prop_section(): A Section properties object stores information about page composition, such as page size, page orientation, borders and margins.
Demographic Table for Example
- Let’s look deep into a demographic table created by
flextablewith details:
- Programming Body
# Import ADaM datasets
adsl<-read_xpt(file.path(path$adam, "adsl.xpt"))
# Factorized categorical variables for dummy
adsl <- adsl |>
mutate(
TRT01P = factor(TRT01P, levels = c("Placebo", "Xanomeline Low Dose", "Xanomeline High Dose")),
AGEGR1 = factor(AGEGR1, levels = c("<65", "65-80", ">80")),
RACE = factor(RACE, levels = c("ASIAN", "WHITE", "BLACK OR AFRICAN AMERICAN", "AMERICAN INDIAN OR ALASKA NATIVE")),
TRTN = fct_recode(as.factor(TRT01PN),
"1" = "54",
"2" = "81",
"3" = "0"
)
)
# Summary Data Frame Function
sumfunc <- function(data, condition, group_var, var, label, decimal) {
...
}
#Categorical Variables
catfunc <- function(data, condition, group_var, catvar, label) {
...
}
#Bind all parts together
final <- bind_rows(...) |>
select(col0, col1, col2, col3)- Default header and footer in formatter paragraphs
# Default headers will be applied in prop_section() argument header_default =.
header_default <- block_list(
fpar(ftext("Summary of Demographic and Baseline Characteristic", fp_text(font.size = 9)),
fp_p = fp_par(text.align = "center")
),
fpar(ftext("(Safety Analysis Population)",fp_text(font.size = 9)),
fp_p = fp_par(text.align = "center")
),
...
)
# Default footers will be applied in prop_section() argument footer_default =.
footer_default <- block_list(
fpar(ftext("Note: This is note 1.", fp_text(font.size = 9)),
fp_p = fp_par(text.align = "left")
),
fpar(ftext("Note: This is note 2.", fp_text(font.size = 9)),
fp_p = fp_par(text.align = "left")
)
)- Properties for template
set_flextable_defaults(
border.color = "#AAAAAA", font.family = "Arial",
font.size = 9, padding = 3, line_spacing = 1
)
sect_properties <-prop_section(
page_size(orient = "landscape"),
page_margins = page_mar(bottom = 0.375,top = 0.75,right = 0.75,left = 0.75, header= 0.75, footer = 0.75, gutter =0),
type = NULL,
section_columns = NULL,
header_default = header_default,
footer_default = footer_default
)- Create flextable and save the customized output in RTF
ft<-final |>
flextable() |>
prepend_chunks(i = ind_num, j = 1, as_chunk("\t")) |>
set_header_labels(row = "", TRTS1 = "Xanomeline Low Dose \n (n = 84)",
TRTS2 = "Xanomeline High Dose \n (n = 84)", TRTS3 = "Placebo \n (n = 86)") |>
autofit() |>
width(j = 2:4, width = 2) |>
width(j = 1, width = 4) |>
align(
j = 2:4,
align = "center",
part = "all"
)
save_as_rtf(ft, path = paste0(getwd(), "/", "t-dm.rtf"), pr_section = sect_properties)Simplify and standarize the programming procedures
TLF-setup.ris a R script contained codes to set up the RTF template and read titles and footnotes from external metadata which should be created and maintained by Lead programmer.Prod/Dev programmers assign the R program/Output names and Linked TLF number at the beginning of program. Then use
source()for template setup as below:
TLF-setup.ris also compatible with our company’s shell and title_footnote metadata.
Alternative method to read mockup by R
read-mockup.ris an alternative method to replaceread_tfl_titlefoot.sasto create metadata including all titles and footnotes in case you want to make the whole procedure with R only.Theoretically, it followed the same internal rules for collecting effective titles and footnotes using internal shell, and generate same data frame which could be applied for both R and SAS production side. But SAS7BDAT is not supported to export from R, so CSV/XLSX will be recommended to use (
haven::write_xpt()may work by not suggested);Use
officer::read_docx()andofficer::docx_summary()function to read mockup shell into data.frame
Batch run and log check scheme
R doesn’t generate such logs like SAS does because most of analysis programming need to assign an object without any echo. And warning message sometimes doesn’t be treated as a red flag.
The new object will not be assigned when unacceptable errors and warnings happen in one step and the whole programs will be suspended here.
We use these features above and
source()our TLF codes in a R markdown file to generate a html document with all echos for review.
Comparison of two methods
| R Markdown + kableExtra | flextable + officer | |
|---|---|---|
| Output TLF Format | Highly Customized PDF | Highly Customized RTF |
| Template Setup | `TLF-start.r` | `TLF-setup.r` |
| Compatible with corporate templates | Yes | Yes |
TLF working procedures
TLF working procedures (expanded)
What’s more is happening?
End-to-End Clinical Reporting Packages
![]() OAK is an open-source community project to evolve software that uses agnostic transformation logic to enable mapping of CDASH to SDTM whose functionality will also generate raw synthetic data.
OAK is an open-source community project to evolve software that uses agnostic transformation logic to enable mapping of CDASH to SDTM whose functionality will also generate raw synthetic data.
![]() To provide an open source, modularized toolbox that enables the pharmaceutical programming community to develop ADaM datasets in R.
To provide an open source, modularized toolbox that enables the pharmaceutical programming community to develop ADaM datasets in R.
What’s more is happening?
End-to-End Clinical Reporting Packages
![]() Serves as a single tool to create SAS transport files and perform pharma specific dataset level validation checks
Serves as a single tool to create SAS transport files and perform pharma specific dataset level validation checks
![]() To represent and exchange R package source code as text files
To represent and exchange R package source code as text files
Study Data Standard is also changing
- Transport v5 file(xpt) to JSON
“CDER and CBER, in collaboration with CDISC and PhUSE, has conducted preliminary testing of CDISC’s Dataset JSON message exchange standard. Initial results indicate potential use as a replacement for XPT v5. As such, CBER and CDER will conduct further testing to evaluate Dataset JSON’s capability to support the submission of regulatory study data. Results will be communicated, and we will engage relevant parties for input as we progress through this evaluation.”
— FDA Study Data Standards Resources Page
Sources
- If you want to know more about:
Thanks










 OAK is an open-source community project to evolve software that uses agnostic transformation logic to enable mapping of CDASH to SDTM whose functionality will also generate raw synthetic data.
OAK is an open-source community project to evolve software that uses agnostic transformation logic to enable mapping of CDASH to SDTM whose functionality will also generate raw synthetic data. To provide an open source, modularized toolbox that enables the pharmaceutical programming community to develop ADaM datasets in R.
To provide an open source, modularized toolbox that enables the pharmaceutical programming community to develop ADaM datasets in R. Serves as a single tool to create SAS transport files and perform pharma specific dataset level validation checks
Serves as a single tool to create SAS transport files and perform pharma specific dataset level validation checks To represent and exchange R package source code as text files
To represent and exchange R package source code as text files